
Light Reflection and Refraction CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:

Convex Mirror Ray diagram, Images Formed with Steps Teachoo
Answer Option 2 shows a convex lens that has no effect on the paths of light rays. We see that these light rays do not cross each other. This means that these rays do not all pass through a single point, which they must do when shown correctly. Option 1 shows the light rays changing direction.

SS Ray Diagrams For Converging Lens Mini Physics Learn Physics Online
Section Key Terms Characteristics of Lenses Lenses are found in a huge array of optical instruments, ranging from a simple magnifying glass to the eye to a camera's zoom lens. In this section, we use the law of refraction to explore the properties of lenses and how they form images.
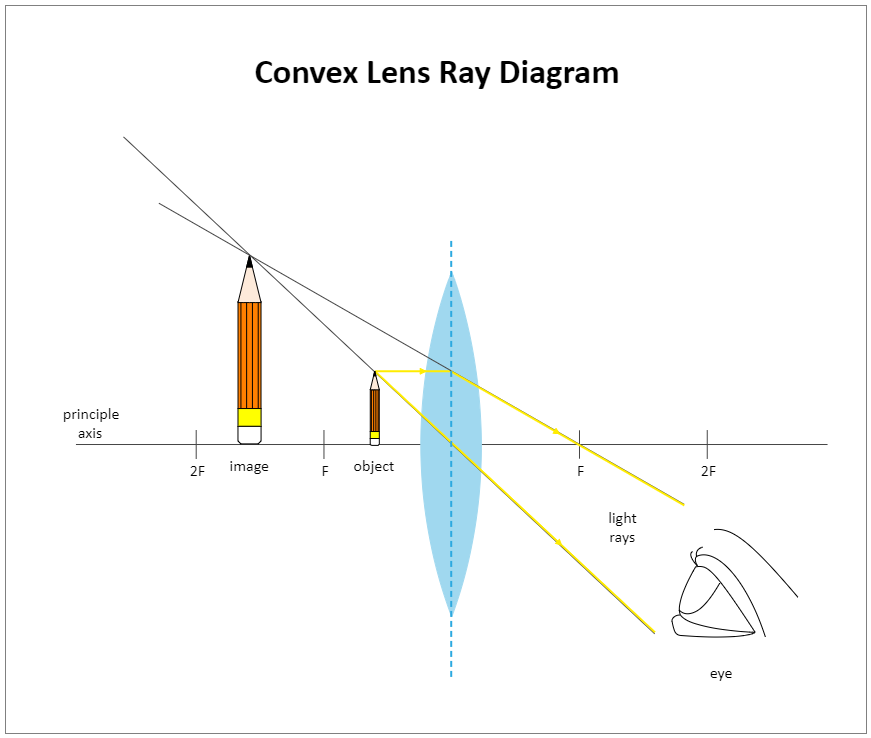
Convex Lens Ray Diagram EdrawMax Template
A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons. The following diagrams show the ray diagrams for convex lens: for objects at different distances from the lens. Describe what is meant by a convex lens? How to draw ray diagrams to show the formation of an image by a convex lens?

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
The convex lens shown has been shaped so that all light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side of the lens. (The axis is defined to be a line normal to the lens at its center, as shown in Figure 1.). The ray diagram in Figure 13 shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as.
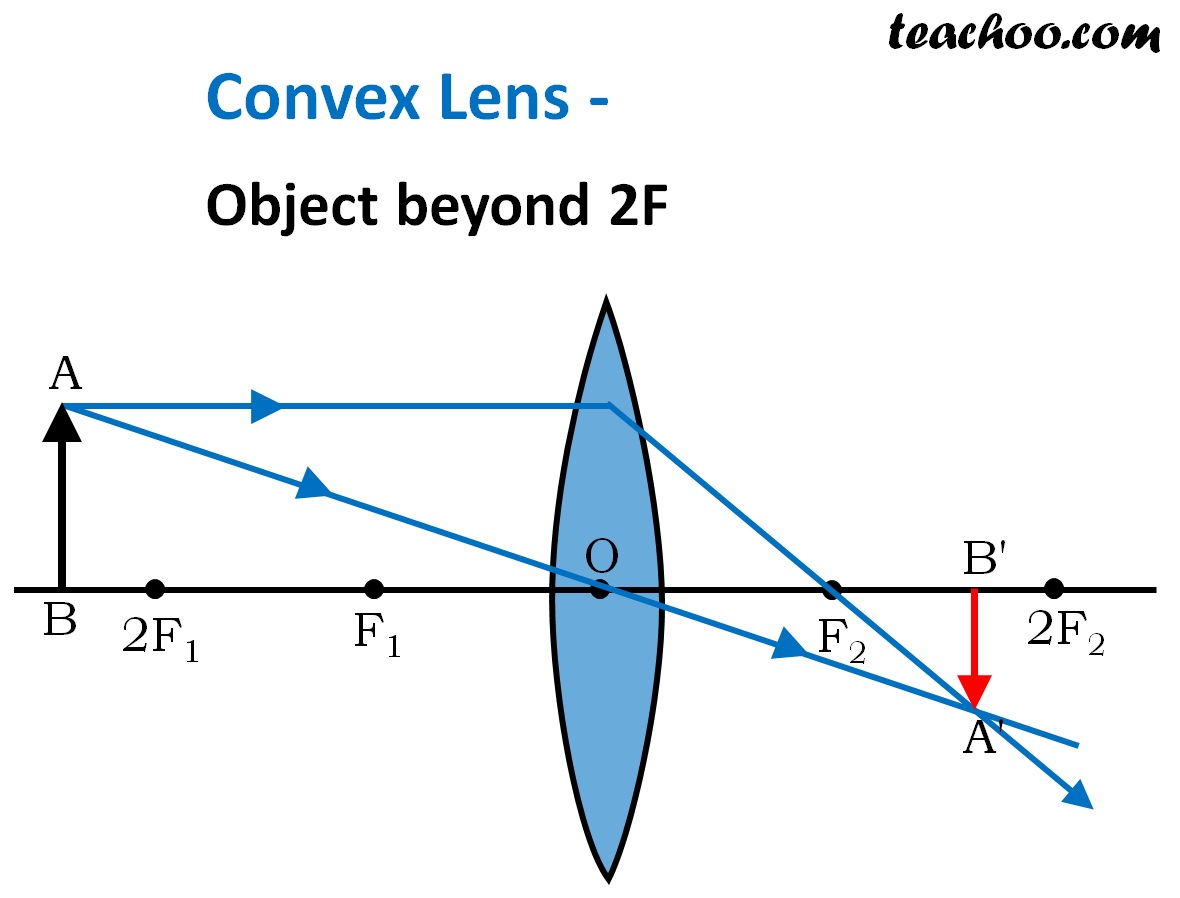
Convex Lens Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table Teachoo
A converging (convex) lens where the object is closer than one focal length from the lens A diverging (concave) lens Note: It doesn't matter if the object is before or after the focal point, the steps followed are still the same. Describe the nature of the image formed Describe the nature of the image formed Give examples of when this
---teachoo.png)
Convex Lens Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table Teachoo
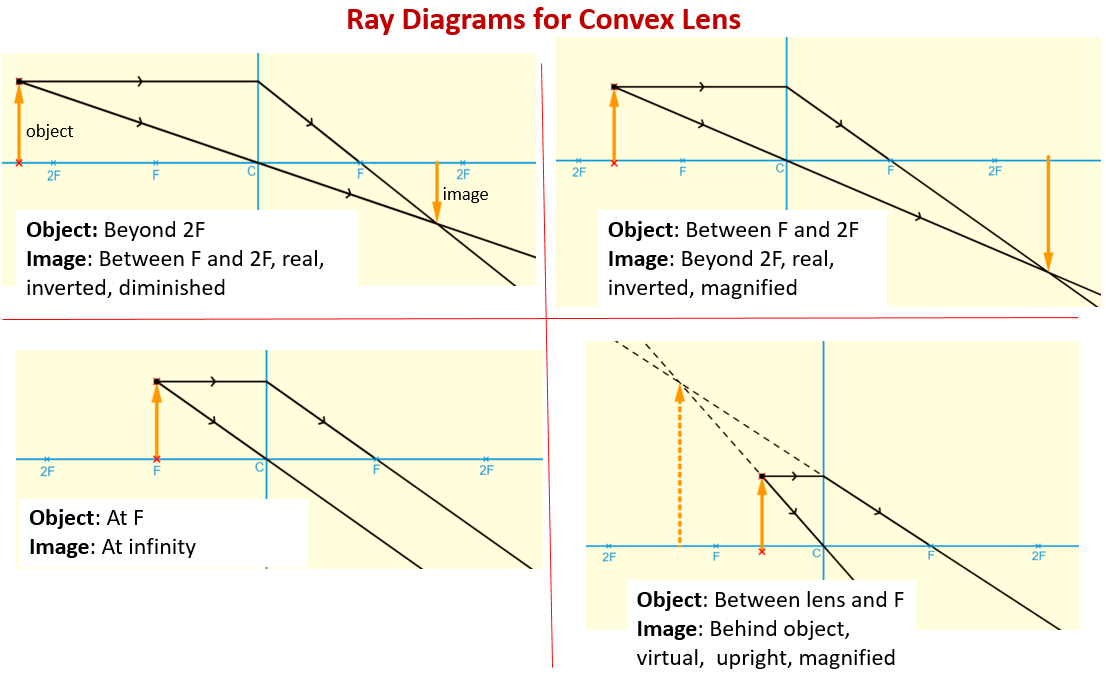
14,248 Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is highly diminished and point size. When an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature, the real image is formed between the centre of curvature and focus.

Ray Diagram Key Stage Wiki
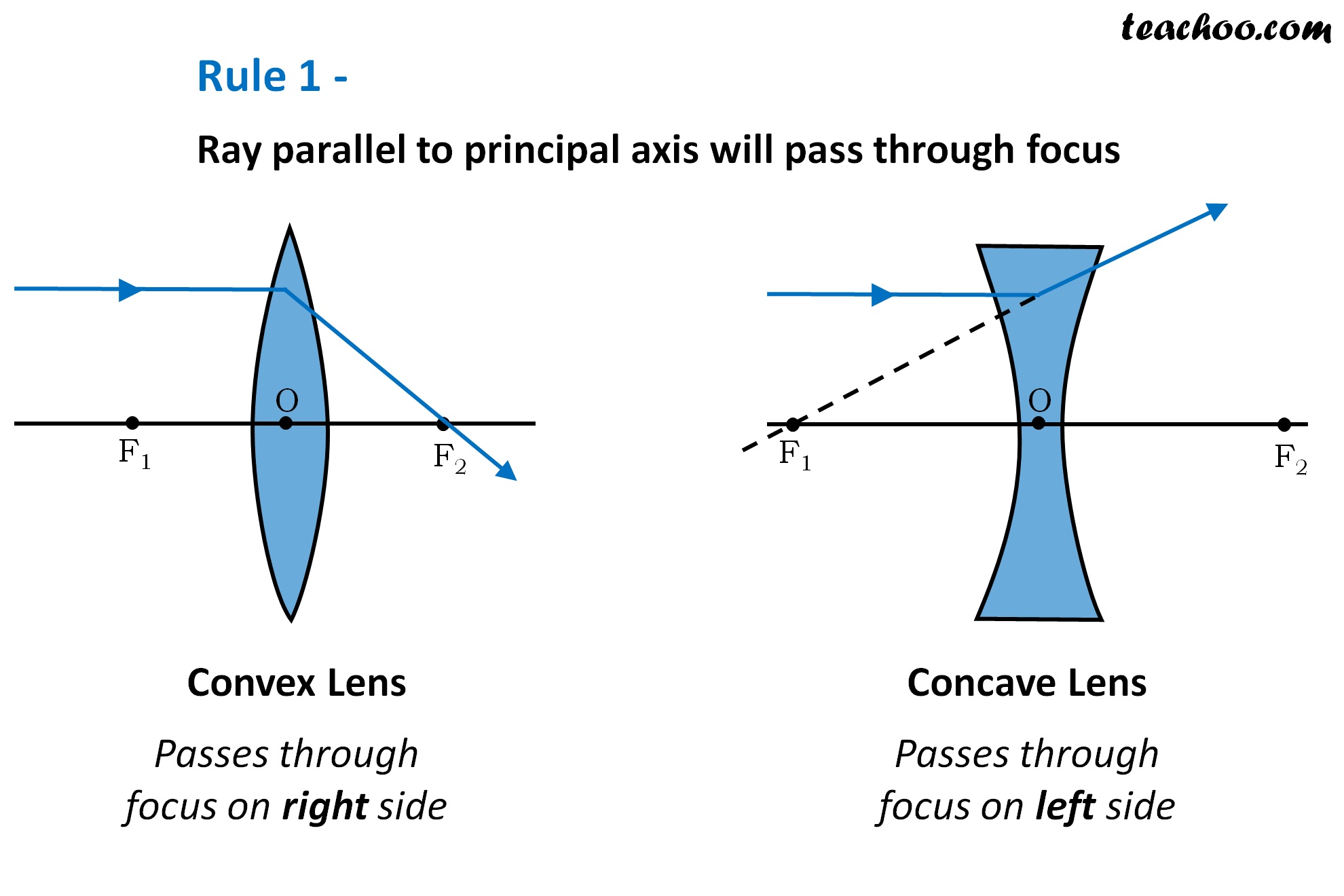
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis So, it passes through focus after refraction We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center So, the ray will go through without any deviation Where both rays meet is point A' And the image formed is A'B' This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2 We can say that Image is Real Image is Inverted

How does convex lens refract light ? Show with diagram
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens.. Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos.

How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10 Physics// YouTube
Types of Lenses The lens shown in the figure is called a concave lens because it is thinner in the middle than at the edges. A concave lens often is called a diverging lens because when surrounded by material with a lower index of refraction, rays passing through it spread out. Ray diagrams for lenses

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
A ray diagram for a convex lens is composed of three principal rays: (1) Ray 1 - A ray is drawn parallel to the principal axis, then refracts and passes through the focal point behind.
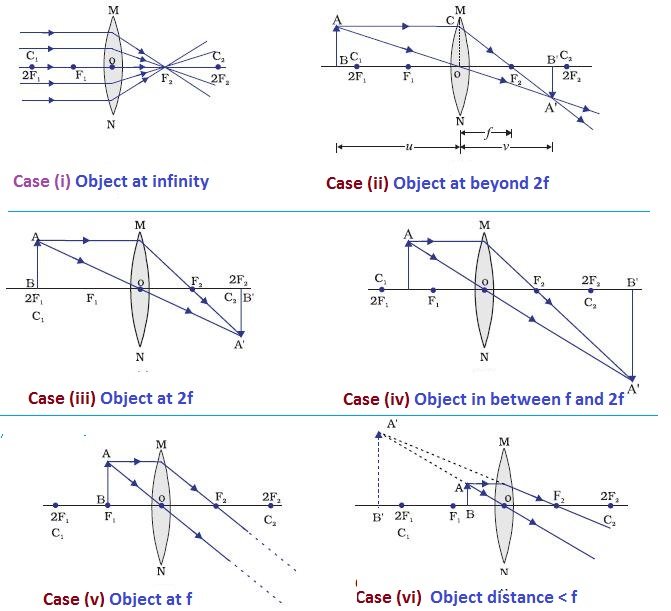
[Get 43+] Image Formation By Convex Lens At F
The power P of a lens is defined as the inverse of its focal length. In equation form: P = 1 f (24.3.9) (24.3.9) P = 1 f. shows the effect of a concave lens on rays of light entering it parallel to its axis (the path taken by ray 2 in the figure is the axis of the lens).

Convex Lens Ray Diagram Heather Murray
A lens is a piece of transparent material which concentrates or disperses light rays when passes through them by refraction. According to the shape and purpose of the lens, they are classified into two types convex lens and concave lens. Let's learn about convex lenses in detail in this article. Table of Contents Definition of Convex Lens
My Physics Webschool Ray Diagram
A light ray traveling through a convex lens experiences refraction when it enters the lens through the front surface and again when it leaves the lens through the back surface. In this diagram here, we have drawn a particularly wide convex lens, which we can use to help us see the effects of the refraction more clearly.
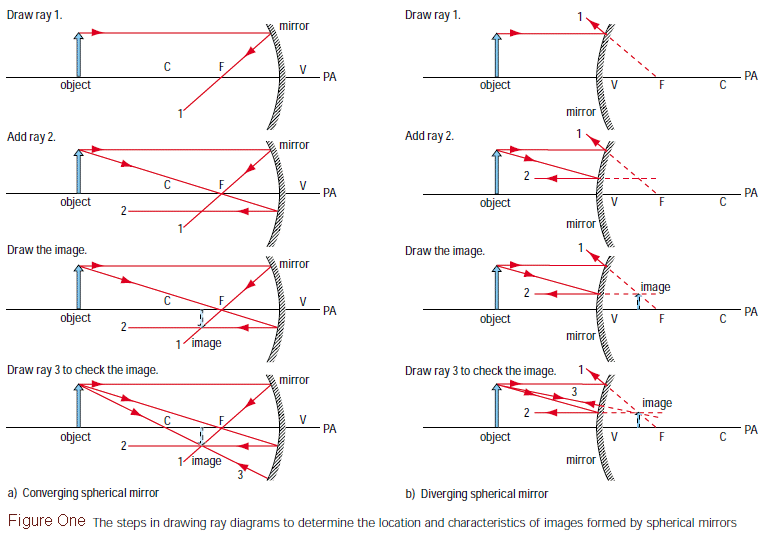
[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams
About Transcript This video explores the concept of convex lenses, focusing on how they refract and transmit light. The instructor explains the behavior of light as it passes through a lens, using the analogy of a car to illustrate refraction. The video also introduces the idea of a lens's focal point and the thin lens assumption.
Convex Lenses and Ray Diagrams (examples, solutions, videos, notes)
Image Formation by lens#convexlensRay diagram of convex lens#concavemirrorImage formation by concave mirror - https://youtu.be/--WXOaOxtv0ray diagram by conc.